A general antibiotic that is used to treat bacterial infections in man. It belongs to the class quinolones of antibiotics and is very effective antibiotic against a variety of bacterial infection affecting the intestines, joints, and intra-abdominal infections, upper and lower respiratory infections, typhoid fever, skin infections, urinary tract infections and other disseminated bacterial infections in man. The drug is also referred to as Cipro, neoflaxin or Ciloxan. The brand name of ciprofloxacin is Proquin. It's mostly tablets which are administered enteral. Can also be as ointment, syrup or liquid.

1. Biomechanics of ciprofloxacin
This is how the drug moves and acts in the body after administration in terms of the organ targeted its therapeutic effects and how it's eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics vary from neonates to adults and depends on the route of administration.
1.1 Route of administration
The route of administration of Cipro are both enteral and parenteral routes
1.2 Absorption
Absorption of Cipro in the small intestine is quite first and the drug is about 70% bioavailable. There is minimum first metabolism of the drug in the intestine making it quite highly bioavailable. To study the amount of drug absorbed serum concentrations are taken 2 hours after the administration of the drug. This is the normal digestion to absorption time. Minimum serum concentration is taken at 12 to 14 hours after the administration of Cipro. There is no absorption when administered IV and the serum concentration is assumed to be 100%
1.3 Food and drug interactions
Different food portrays different effect on the oral dose of Cipro. For instance when in an experiment where Cipro was orally administered after intake of nalta jute a type of fibrous food the rate of dissolution of the drug in was greatly reduced. Notably, the rate of the disintegration of the drug was greatly reduced. This is because to reduced increased bowel movement as nalta jute is a fiber. Generally, this will reduce the bioavailability of the drug, therefore, reduced therapeutic effects. Also, reduced disintegration is due to ph. variation.
1.4 Bioavailability
Bioavailability is the amount of drug that reaches the blood from the route of administration. It's highest when administered intravenously and is estimated to be 100% bioavailable. On the other hand, when administered orally bioavailability reduces to about 70% only this is due to the effect of digestion process in the intestines which gradually reduces the amount of the drug making it to the blood through absorption. When administered intravenously, for instance, 400mg of the drug will produce the same serum concentration as when 500mg of the drug is administered orally when measured after two hours.
1.5 Distribution
This is the movement of the drug from site of administration to the site of action or to the therapeutic sites. For drugs to move from the site of administration they don't move as free molecules, they will bind to the serum proteins which will aid its movement in blood. The concentration of the binding to serum proteins will determine the amount of drug distributed in the blood. For instance, in our case ciprofloxacin binds to about 20 to 40% of the total blood serum proteins which is slightly low compared to other drugs. Distribution of Cipro is quite widely spread and the effect is not specific. Due to this high distribution rate, there are increased cases of tissue concentration of Cipro than serum concentration. This makes it a good broad-spectrum antibiotic. Concentration is seen high in genital tissues, mucus, and saliva. The drug also is distributed to the CSF.
1.6 Metabolism
This is the subsequent breakdown of the drug after its therapeutic function id done. Usually, the metabolites of a drug can have more no therapeutic function, have a reduced therapeutic function or an increased therapeutic function. Ciprofloxacin, in this case, the metabolite is seen in urine which is about 15% of the orally administered dose. The metabolite is still therapeutic or has an antibiotic function but its reduced function as compared to the drug itself.
1.7 Excretion
It's the final removal of the drug metabolite from the body. Excretion of the drug depends on the renal function and is reduced in renal impairment. In normal condition, the half-life of Cipro is about 4 hours and it clears from the blood in about 24 hours after administration. The rate of renal of renal clearance is about 30 microgram per minute.
Of great importance to note is that 30 to 40 % of Cipro is excreted unchanged in urine. This is the reason why the urine is still antimicrobial in nature even though the effect is reduced.
Drug to drug to drug interaction may affect the excretion of Cipro. For instance, when Cipro is co-administered with probenecid it reduces renal clearance by about 50%. This lead to the increased therapeutic effects of the drug and side effects.
The drug is also excreted in feces especially in a situation of increased biliary concentrations. About 20% of Cipro is recovered in feces 5 days after oral administration.
1.8 drug-drug interactions
This is the effect of the drugs on the pharmacokinetics of other drugs. It may be those like reduced or increased absorption, metabolism and therapeutic effects which can be antagonistic or synergistic in nature.
When Cipro is administered together with food there is a reduced rate of absorption of the drug leading to time to peak concentration from 1 hour to 2 hours. However other pharmacokinetics of Cipro is not affected after administration.
When Cipro is administered together with Theophylline it leads to reduced rate of clearance of theophylline from blood thus high theophylline serum concentration. This may lead to increased risk of patient developing CNS disorders and side effects of the drug. The pharmacist or the physician should advise on the administration of these two drugs.
Age and ciprofloxacin therapy
In patients who are above the age of 65 years, there is marked increase plasma concentration after oral administration 15 to 40% serum concentration as compared to the young population. This is due to the reduced renal function in elderly.
In patients with liver cirrhosis studies show that there are reduced effects on the pharmacokinetics of the drug.
Mode of action
Ciprofloxacin has a wide effect on the gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
Like other quinolones, it acts mainly by enzyme inhibition. It inhibits the enzyme topoisomerase II and topoisomerase IV, this leads to inhibition of the bacterial DNA synthesis, recombination, and synthesis. This mode of action makes quinolones and ciprofloxacin an ideal antibiotic against drug-resistant bacteria to penicillin and other beta-lactam drugs. Co-administration with other antimicrobials can be done as there is no cross-resistance reported between ciprofloxacin and other antimicrobial agents.
It's highly effective against staphylococcal, Proteus, enterobacteria, Hemophilus influenza and parainfluenza, pseudomonas and salmonella infections.
Susceptibility tests
These are tests done to study the bacterial species susceptible to ciprofloxacin. A piece of sterile paper is soaked in ciprofloxacin solution and then placed in media in which bacterium has been cultured. It produces regions of inhibitions about 15mm in diameter in susceptible strains. The higher the diameter the higher the susceptibility of the strain to the drug.
Indications
The physician may prescribe the drug to patients who have STI due to Proteus bacteria, Providencia and E. coli
Stricture formation and skin infections can also be a reason for indication
Gastrointestinal tract infections by enterobacteria
Contraindication
- Contraindications should be done to patients who portray allergic reactions to ciprofloxacin and other quinolones.
- In pediatrics less than 18 months old they should be prescribed in case of complicated STI or other complicated infections.
- Patients who portray CNS side effects such as confusions should not be indicated for ciprofloxacin.
- Patients who are administered with Theophylin should not be given ciprofloxacin as cases of fatality have been reported.
Adverse effects
These are undesired drug effects, they may include
- A headache, abdominal, foot, joint and extremities pain.
- Cardiovascular effects such as palpitation, arterial and ventricular atrophy, hypertension among others
- CNS effects such as insomnia, dizziness, and loss of control.
- GIT effects such as candidiasis of the mouth and pain of the mucosa
- Blurred vision and photophobia.
- Skin pruritis and urticaria.
Bones and joints infection
Bones and joints infections are to be serious and not something that someone can adhere. They might be hazardous or related with long haul inability and decreased personal satisfaction. The range of malady has changed after some time and the extent of iatrogenic illness caused by prosthetic joints is expanding every year.
Osteomyelitis or Bones infection is caused when microscopic organisms colonize bone, as a rule a sterile tissue, by means of direct immunization from injury or activity. Whereas joint infection can be a result of the bone infection, especially that happen with children.
Diagnosis requires clinical side effects, fitting radiological imaging and microbiological inspecting. In addition extremely restricted bones infections might be dealt with antibiotics alone, with a possibility of a planned surgery is to be a must for some contaminations.
Antibiotics as curing methods for Bones and joints infection
The principle of our method is administering antibiotics directly to the affected area in much higher concentration than usual - without negative impact on the rest of the body. At the same time existing defects of the bone are reconstructed. If necessary, implants can be combined immediately and thus restore the original function quickly.
Bones infection
Infections of the bone also called osteitis or the bone marrow osteomyelitis are among the most difficult diseases to treat. While in the past numerous operations and months of hospitalization were required, today a single operation followed by a brief hospitalization is usually sufficient.
Osteomyelitis is the most remarkable bone infection disease, which happen typically by a discharge shaping microscopic organisms. Generally the microorganisms enter the bone by damage by a sharp protest, open break, or by the circulation system. In a result to that, both the bone and the bone marrow might be contaminated.
The place of disease can be anyplace in the body. But, especially in the long bones in the children are generally influenced. Concerning grown up people the vertebrae and the pelvis are most ordinarily influenced.
Osteomyelitis has a tendency to happen close to the joints of the appendages. It has side effects incorporate; profound torment and muscle fits in the zone of aggravation, redness, as well as warmth and fever.
What causes Bones infections?
Microorganisms are to be found in the blood and are exceptionally basic in adolescence. This can come about because of different diseases. We can mention, from the ear, nose, throat, or it can be as well from brushing the teeth.
More often, immune system gains the battle, and the microscopic organisms are to be cleared from the blood. But, if there are a lot of microorganisms in the blood as well as sufficiently solid, it can contaminate the bone.
How it is been treated?
The bone treatment is bed rest in hospital while taking Antibiotics, typically intravenously, and once in a while surgical debridement or surgery to expel dead bone tissue.
Joints Infections
One of the most infections of the joint is Septic arthritis. It is also called infectious or bacterial arthritis, pyarthrosis as well as suppurative arthritis. Septic joint inflammation happens when a microbe spreads through the circulatory system to a joint. Manifestations may incorporate redness, warmth and irritation around the influenced zone. In addition, an individual may encounter firmness, loss of scope of movement as well as fever.
Diagnosis is set by investigation of liquid that has been expelled from the joint.
What are the causes?
The infection causes are somehow different to recognize and not been comprehended yet. In more often cases, the immune system and the joint can wipe out bacterial contamination before it overpowers the body. Yet, in the event that the microbes are especially solid as well as substantial in number, in this case it might overpower the joint and cause a serious disease.
There is also main other factor that causes joint infection, is the contamination from a bone can cross into a joint. This usually happens in four areas - the hip, shoulder, elbow, and lastly Ankle.
How it is been treated?
Because of the seriousness of the joint infection, many clinics, and doctors has worked to maintain and help improve different possible ways to treat and cure Joint infection. Among the most used and effective treatment is by Antibiotics.
Joint infection treatment is done by pharmaceutical antibiotics and part of tainted joint liquid. It can be also a mix of surgery and antibiotics.
This infection most happen to children, and because they are most sensitive and most affected, it can be both joint and bone infection. And like different contaminations, antibacterial agents are the essential treatment. In the event that the disease includes a youngster's joint, in this case surgery might be important to wipe out the joint to avert cartilage harm. On the off chance that the contamination also includes the bone it has to be a must bone surgery.
Lexapro (escitalopram) is a medication commonly prescribed to treat depression and anxiety disorders. It belongs to a class of drugs known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Lexapro works by increasing the level of serotonin in the brain, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood. By improving serotonin balance, it can reduce feelings of sadness, worry, and emotional tension. The medication may also help improve sleep, appetite, and overall daily functioning. Its therapeutic effects usually develop gradually over several weeks of regular use. Some patients may experience mild side effects, especially during the first days of treatment. You can buy Lexapro without prescription in the USA online on the website my-depression-treatment.com.
 infections
infections
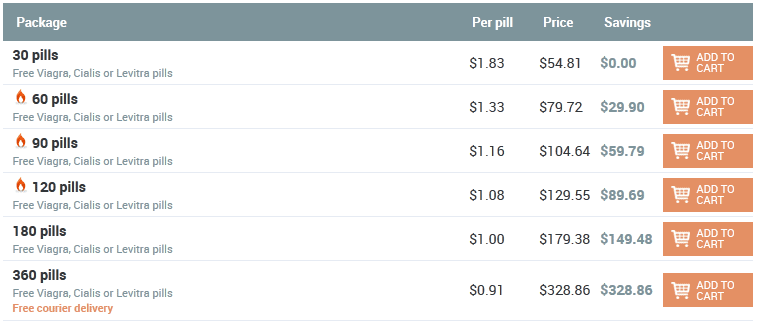
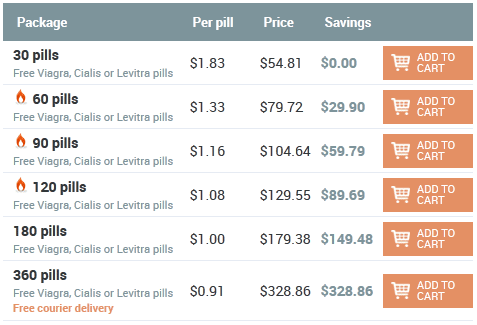
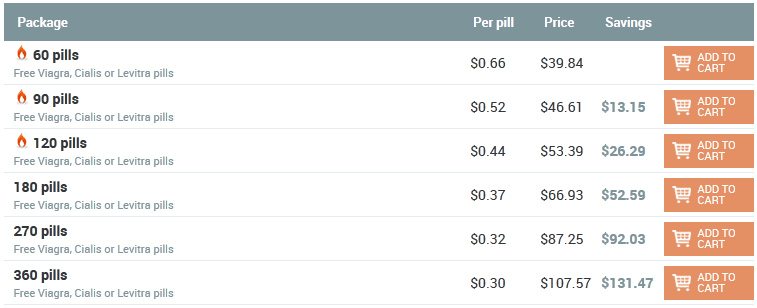
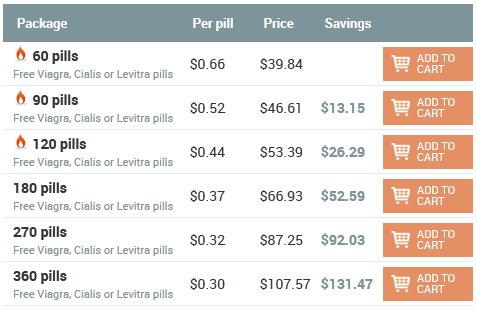
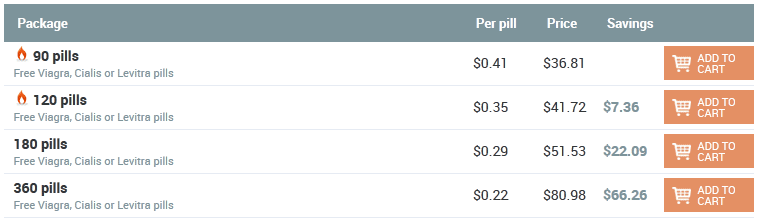


John 20:05:35 25/12/25
Hello! I'm worried about prostatitis, very severe pain. Friends advised me to this store. I ordered cipro for the treatment of prostatitis. He helped me a lot, the pain was gone! There were no side effects, and I am very happy ... The order came quickly !!! Thank!!!