What is Hookworm Disease?
Ancylostomidoses – helminthiasis caused by ankilostomida; distinguished hookworm (pathogen – hookworm) and necatoriasis (pathogen – necator). Both helminthiasis have a similar clinical picture.
Ankilostomidozy are distributed mainly among the population of the tropical and subtropical zones in the countries of South and Central America, South Asia and Africa. In some of these countries, up to 50% of the population is infected. Hookworm foci are also found in southern Europe (for example, in Italy). Hooks of hookworm are registered in some regions of Georgia and Azerbaijan.
The source of infection of Ancylistoma duodenale is sick people, and Ancylostoma braziliens – mainly dogs and cats. The natural susceptibility of people is high. Infection occurs through fruits contaminated with soil, vegetables, greens, and berries, where hookworm larvae can be found, and when walking barefoot, resting on the ground, necator can penetrate into the human body. Ways of transmission of helminthiasis are food, drinking and contact way. Endemic foci are formed in coal and mining mines with high ambient temperature, humidity and poor sanitary conditions. Risk groups include summer residents, miners, agricultural workers.
Children are most at risk of infection. They often go barefoot and poorly follow the rules of personal hygiene.
Causes of Hookworm
Ankilostomy pathogens are two closely related species of roundworms (nematodes): hookworm (Ancylostoma duodenale) and necator (Necator americanus) related to geohelminths. Hook size: male length 8-11 mm, females 10-14 mm; necator dimensions: male length 5–9 mm, females 9–12 mm. Mature ankilostomida live in the upper part of the small intestine of man.
Pathogenesis during Ankilostomidosis
The life cycle begins with the eggs in the soil along with faeces. The development of larvae is possible at a temperature of 14-40 ° C (optimum temperature of 28-30 ° C) and high soil moisture.
After 7-10 days, the larvae take the form of a filarial with a cylindrical esophagus and become infectious. Larvae actively move in the soil in horizontal and vertical directions. When human skin is in contact with soil, the larvae, attracted by body heat, actively penetrate the host’s body through the skin. Then they penetrate into the blood vessels and move along them to the right atrium, then to the pulmonary artery and the capillaries of the pulmonary alveoli. Tearing the walls of capillaries, they enter directly into the alveoli and through the airways penetrate the pharynx.
With saliva, the larvae are ingested by the host and enter the duodenum, where their further development to the mature stage occurs. The larvae they produce come out with feces. After 8-10 weeks after infection, the sexually mature helminth eggs are secreted from the body of the sick person. A sick person is not an immediate danger to others, because at the time of the release of eggs from the body do not have an invasive ability. It is necessary ripening helminth eggs in the soil. The life of the cathead goes up to 4-5 years, nekator- up to 15 years.
The source of the invasion is only man. The dispersal of larvae in the environment is facilitated by soil contamination with faeces, washing out of cesspools by storm rains, and the use of non-infected feces for fertilizing vegetable gardens. Human infection with ankilostomy occurs through contact with the soil in areas unfavorable to this helminthiasis (walking barefoot, lying on the ground, doing agricultural and earthworks), eating vegetables, fruits, and greens contaminated with feces containing ankylostomid larvae through dirty hands. In the subtropics, the soil in most foci during the winter is completely cleared of larvae, therefore, infection of people occurs in a certain season, lasting about 6 months.
During the migration of larvae, sensitization of the human body by products of their metabolism and decay occurs. The result is a rash on the skin, itching, bronchitis, bronchopneumonia, blood eosinophilia up to 30-60%.
Symptoms of Hookworm
The incubation period of the disease lasts 40-60 days. In most cases, the disease is asymptomatic. In more severe cases, the symptoms depend on how the parasites enter the body.
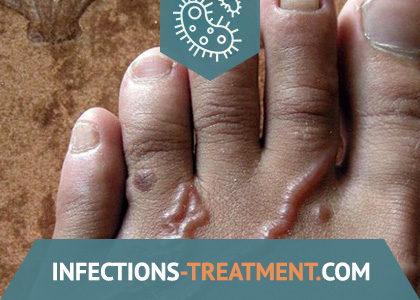
When penetrating through the skin, itching and burning of the skin, various kinds of rash (erythematous, papular, vesicular, pustular) occur, which can persist for several months. Massive invasion leads to swelling of the limbs. During the migration of larvae through the respiratory tract may develop catarrhal phenomena, shortness of breath, wheezing, possible development of bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia. At a later stage, when it enters the gastrointestinal tract, duodenitis develops with heartburn, lack of or increased appetite, sometimes taste perversion (desire to eat, for example, clay), nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastric and liver regions, often accompanied by diarrhea.
The most characteristic manifestation of the disease is hypochromic iron deficiency anemia. Ankylostoma feeds on blood. It is attached to the walls of the intestinal mucosa by the teeth. At the place of fixation of the helminth, erosion and ulcers up to 2 cm in diameter occur, and long-term intestinal bleeding may occur, which cause the development of iron deficiency anemia. Blood protein decreases (hypoalbuminemia).
The central nervous system is affected, lethargy, mental retardation and physical development appear.
Consequences of paratyzing
Chronic ankilostomosis is manifested by weakness, dizziness, epigastric pain, weight loss, edema. Since the hookworm feeds on blood, it attaches to the intestinal wall mucosa with teeth, where bleeding ulcers are formed, reaching 2 cm in diameter. Due to chronic blood loss, hypochromic iron deficiency anemia develops, the blood protein decreases (hypoalbuminemia). The central nervous system is affected, lethargy, mental retardation and physical development appear. In severe cases, death is possible.
Diagnosis of Hookworm
The diagnosis is based on the detection of eggs in the contents of the duodenum obtained by sensing, and in feces, as well as on the results of serological reactions – hemagglutination, latex-agglutination. In the blood, there is a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and the number of erythrocytes to 1 000 000-800 000 in 1 μl of blood with a decrease in the color index to 0.3-0.5, an increase in ESR, and eosinophilia.
Treatment of Hookworm
In the treatment of ankilostomidoz use naftamon. The drug is prescribed inside. Daily dose for adults 5 g. Accepted on an empty stomach 1 hour before breakfast. Powder poured into 50 ml of warm sugar syrup, mix thoroughly and drink in one step. Assign for 5 days. The tool is contraindicated in diseases of the liver. Thymol treatment involves the appointment of the patient as a mandatory diet with restriction of fat and alcohol. The day before give saline laxative. In the morning of the fasting day treatment, timol capsules are prescribed – 4 g. This amount of the drug is divided into four parts and given one after the other with an interval of 20 minutes. After 1.5 h, give saline laxative. Treatment spend 3 days in a row. It is possible to repeat the course after 3 weeks. The drug is contraindicated in cardiac decompensation, liver and kidney diseases.
Prevention of Hookworm
For prophylaxis, it is necessary to wash vegetables, fruits, berries thoroughly before use, do not drink unboiled water, wear shoes in likely places of soil contamination with fecal matter. To destroy the larvae in the soil in small areas are treated with salt or boiling water.